DOI:
https://doi.org/10.64539/msts.v1i2.2025.370Keywords:
Overfitting, Regularization, L1/L2 Penalties Dropout, Machine Learning, GeneralizationAbstract
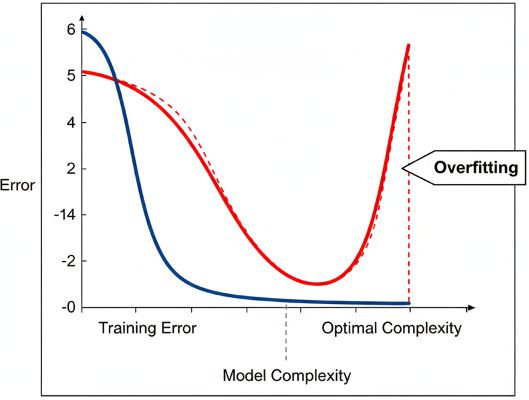
One of the most serious issues in the current predictive modelling is overfitting, especially with the increase in the complexity and size of machine learning systems. This research proposes regularisation-based methods as critical methods of enhancing generalisation and avoiding noise memorization in training data by models. The systematic literature review of the study that includes 2006-2025 research provides the synthesis of classical regularization methods, including L1/L2 penalties, Elastic Net, dropout, and early stopping, and emerging methods, including probabilistic dropout variants, Bayesian regularization, adaptive regularizers, and hybrid frameworks. The review points to the importance of the regularisation in the context of increasing the performance of generalisation, enhancing robustness to noisy or finite-sized datasets, stabilising optimization dynamics, and interpretability in high dimensional computations. It also determines the major shortcomings in the extant research such as, lack of comprehension on implicit regularisation, the cross domain comparative assessment and the requirement of adaptive and automatic strategies of regularisation. The paper ends with the research recommendations and open directions of research that are meant to enhance the theory, diagnostic tools, and towards the practitioners to effective regularisation configurations under different data regimes. Altogether, this paper gives an integrative and holistic approach to regularisation as a core building block of constructing credible, robust and general predictive models.
References
[1] C. Zhang, S. Bengio, M. Hardt, B. Recht, and O. Vinyals, “Understanding deep learning requires rethinking generalization,” arXiv preprint arXiv:1611.03530, 2016. [Online]. Available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1611.03530
[2] Y. Tian and Y. Zhang, “A comprehensive survey on regularization strategies in machine learning,” Information Fusion, vol. 80, pp. 146–166, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2021.11.005.
[3] I. S. C. Umerah, U. A. Tochukwu, A. Maduabuchuku, O. M. Nwakeze, and O. C. Akachukwu, I. S. Chinasa “AI-driven diagnostic imaging: Hybrid CNN-GNN models for early detection of cancer from pathological images,” Int. J. Latest Technol. Eng., Manag. Appl. Sci., vol. 14, no. 9, pp. 579–588, 2025. https://doi.org/10.51583/IJLTEMAS.2025.1409000070.
[4] R. Moradi, R. Berangi, and B. Minaei-Bidgoli, “A survey of regularization strategies for deep models,” Artif. Intell. Rev., vol. 53, no. 6, pp. 3947–3986, 2020, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-019-09784-7.
[5] N. Srivastava, G. Hinton, A. Krizhevsky, I. Sutskever, and R. Salakhutdinov, “Dropout: A simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting,” J. Mach. Learn. Res., vol. 15, pp. 1929–1958, 2014. https://dl.acm.org/doi/abs/10.5555/2627435.2670313.
[6] T. Chen and C. Guestrin, “XGBoost: A scalable tree boosting system,” in Proc. 22nd ACM SIGKDD Int. Conf. Knowl. Discov. Data Min., San Francisco, CA, USA, 2016, pp. 785–794. http://dx.doi.org/10.1145/2939672.2939785.
[7] J. Kolluri, V. K. Kotte, M. S. B. Phridviraj, and S. Razia, “Reducing overfitting problem in machine learning using novel L1/4 regularization method,” in Proc. 4th Int. Conf. Trends Electron. Informatics (ICOEI), IEEE, 2020, https://doi.org/10.1109/ICOEI48184.2020.9143022.
[8] A. Pak, A. K. Rad, M. J. Nematollahi, and M. Mahmoudi, “Application of the Lasso regularisation technique in mitigating overfitting in air quality prediction models,” Sci. Rep., vol. 15, art. no. 547, 2025, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-84342-y.
[9] G. C. Cawley and N. L. C. Talbot, “Preventing over-fitting during model selection via Bayesian regularisation of the hyper-parameters,” J. Mach. Learn. Res., vol. 8, pp. 841–861, 2007, https://dl.acm.org/doi/abs/10.5555/1248659.1248690.
[10] M. Ghayoumi, “Enhancing efficiency and regularization in convolutional neural networks: Strategies for optimized dropout,” AI, vol. 6, art. no. 111, 2025, https://doi.org/10.3390/ai6060111.
[11] X. Ying, “An overview of overfitting and its solutions,” J. Phys.: Conf. Ser., vol. 1168, no. 2, art. no. 022022, 2019, https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1168/2/022022.
[12] P. Zhang, S. Zhang, X. Liu, L. Qiu, and G. Yi, “A least squares ensemble model based on regularization and augmentation strategy,” Appl. Sci., vol. 9, art. no. 1845, 2019, https://doi.org/10.3390/app9091845.
[13] I. Marin, A. Kuzmanic Skelin, and T. Grujic, “Empirical evaluation of the effect of optimization and regularization techniques on the generalization performance of deep convolutional neural network,” Appl. Sci., vol. 10, art. no. 7817, 2020, https://doi.org/10.3390/app10217817.
[14] A. Kanavos, M. Trigka, E. Dritsas, G. Vonitsanos, and P. Mylonas, “A regularization-based big data framework for winter precipitation forecasting on streaming data,” Electronics, vol. 10, art. no. 1872, 2021, https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10161872.
[15] T. Kotsilieris, I. Anagnostopoulos, and I. E. Livieris, “Regularization techniques for machine learning and their applications,” Electronics, vol. 11, art. no. 521, 2022, https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11040521.
[16] A. B. Shanmugavel et al., “A novel ensemble-based reduced overfitting model with convolutional neural network for traffic sign recognition system,” Electronics, vol. 12, art. no. 926, 2023, https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12040926.
[17] F. Jin, X. Chen, Y. Yu, and K. Li, “An improved regularization stochastic configuration network for robust wind speed prediction,” Energies, vol. 18, art. no. 6170, 2025, https://doi.org/10.3390/en18236170.
[18] A. Mohammad-Djafari, “Regularization, Bayesian inference, and machine learning methods for inverse problems,” Entropy, vol. 23, art. no. 1673, 2021, https://doi.org/10.3390/e23121673.
[19] S. Gupta, R. Gupta, M. Ojha, and K. P. Singh, “A comparative analysis of various regularization techniques to solve overfitting problem in artificial neural network,” in Proc. REDSET 2017, CCIS, vol. 799, Springer, 2018, pp. 363–371, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-8527-7_30.
[20] F. Ahmadi Abkenari, A. Milani Fard, and S. Khanchi, “Hybrid machine learning-based approaches for feature and overfitting reduction to model intrusion patterns,” J. Cybersecurity Privacy, vol. 3, no. 3, pp. 544–557, 2023, https://doi.org/10.3390/jcp3030026.
[21] X. Zhang, L. Sun, and L. Qi, “Bayesian regularization algorithm based recurrent neural network method and NSGA-II for the optimal design of the reflector,” Machines, vol. 10, art. no. 63, 2022, https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10010063.
[22] M. Liu, G. Srivastava, J. Ramanujam, and M. Brylinski, “Insights from augmented data integration and strong regularization in drug synergy prediction with SynerGNet,” Mach. Learn. Knowl. Extr., vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 1782–1797, 2024, https://doi.org/10.3390/make6030087.
[23] M. Xiao et al., “Addressing overfitting problem in deep learning-based solutions for next generation data-driven networks,” Wireless Commun. Mobile Comput., vol. 2021, art. ID 8493795, pp. 1–10, 2021, https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/8493795.
[24] C. F. G. Santos and J. P. Papa, “Avoiding overfitting: A survey on regularization methods for convolutional neural networks,” ACM Trans. Comput. Syst., vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 1–27, 2018, https://doi.org/10.1145/1122445.1122456.
[25] C. M. Bishop, Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning. New York, NY, USA: Springer, 2006. https://link.springer.com/9780387310732.
[26] I. Goodfellow, Y. Bengio, and A. Courville, Deep Learning. Cambridge, MA, USA: MIT Press, 2016. https://synapse.koreamed.org/pdf/10.4258/hir.2016.22.4.351.
[27] M. Belkin, D. Hsu, S. Ma, and S. Mandal, “Reconciling modern machine-learning practice and the classical bias–variance trade-off,” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, vol. 116, no. 32, pp. 15849–15854, 2019, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1903070116.