DOI:
https://doi.org/10.64539/msts.v1i2.2025.44Keywords:
Heart Failure, Health, Machine Learning, K-Nearest Neighbors, PredictionAbstract
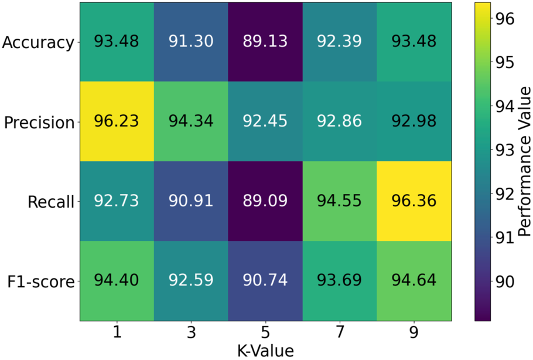
Heart failure is a cardiovascular disease with a high mortality rate and tends to increase every year. Therefore, a method is needed that can help the process of classifying heart failure quickly and accurately. This study aims to design and implement a heart failure classification system using the K-Nearest Neighbor (K-NN) machine learning method. The dataset used consists of 918 patient data with eleven input variables and two output classes, namely patients diagnosed with heart failure and patients not diagnosed with heart failure. The research stages include data loading, dividing training data and test data, implementing the K-NN algorithm with various K values, and evaluating model performance using accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score metrics. The test results show that variations in the K value have a significant effect on the performance of the classification model. The K value = 9 produces the best performance with an accuracy of 93.48%, a recall of 96.36%, and an F1-score of 94.64%, which indicates a good balance between precision and recall. Based on these results, the K-NN method with a value of K = 9 is recommended as the optimal configuration in the classification of heart failure disease in this study.
References
[1] M. A. L. Suratri, “Pengaruh Hipertensi Terhadap Kejadian Penyakit Jaringan Periodontal (Periodontitis) pada Masyarakat Indonesia (Data Riskesdas 2018),” Bul. Penelit. Kesehat., vol. 48, no. 4, pp. 227–234, 2020, https://doi.org/10.22435/bpk.v48i4.3516.
[2] P. Ghosh et al., “Efficient Prediction of Cardiovascular Disease Using Machine Learning Algorithms With Relief and LASSO Feature Selection Techniques,” IEEE Access, vol. 9, pp. 19304–19326, 2021, https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3053759.
[3] I. Dilalah, H. Christiandari, J. Y. Hernawan, dan E. Suprasetya, “Optimizing Cardiovascular Disease Medication Awareness: A Community Engagement Initiative at Posbindu Kenanga 3 Manggulan”, Jurnal Pengabdian Masyarakat Permata Indonesia, vol. 3, no. 2, pp. 75–81, 2023, https://jurnal.permataindonesia.ac.id/index.php/JPMPI/article/view/243.
[4] A. U. Haq, J. P. Li, M. H. Memon, S. Nazir, R. Sun, and I. Garciá-Magarinõ, “A Hybrid Intelligent System Framework for the Prediction of Heart Disease using Machine Learning Algorithms,” Mob. Inf. Syst., vol. 2018, p. 3860146, 2018, https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/3860146.
[5] C. J. Taylor, R. Ryan, L. Nichols, N. Gale, F. D. Richard Hobbs, and T. Marshall, “Survival following a diagnosis of heart failure in primary care,” Fam. Pract., vol. 34, no. 2, pp. 161–168, 2017, https://doi.org/10.1093/fampra/cmw145.
[6] B. Chulde-Fernández et al., “Classification of Heart Failure Using Machine Learning: A Comparative Study,” Life, vol. 15, no. 3, pp. 1–18, 2025, https://doi.org/10.3390/life15030496.
[7] L. N. Farida and S. Bahri, “Klasifikasi Gagal Jantung menggunakan Metode SVM (Support Vector Machine),” Komputika J. Sist. Komput., vol. 13, no. 2, pp. 149–156, 2024, https://doi.org/10.34010/komputika.v13i2.11330.
[8] R. S. Nurhalizah, R. Ardianto, and P. Purwono, “Analisis Supervised dan Unsupervised Learning pada Machine Learning: Systematic Literature Review,” J. Ilmu Komput. dan Inform., vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 61–72, 2024, https://doi.org/10.54082/jiki.168.
[9] S. L. Karri, L. C. De Silva, D. T. C. Lai, and S. Y. Yong, “Classification and Prediction of Driving Behaviour at a Traffic Intersection Using SVM and KNN,” SN Comput. Sci., vol. 2, no. 3, 2021, https://doi.org/10.1007/s42979-021-00588-7.
[10] S. Tiwari, “Supervised Machine Learning: A Brief Introduction,” Proc. Int. Conf. Virtual Learn., vol. 17, no. 5, pp. 219–230, 2022, https://doi.org/10.58503/icvl-v17y202218.
[11] L. Puig, “On the reduction of Alperin’s Conjecture to the quasi-simple groups,” J. Algebr., vol. 328, no. 1, pp. 372–398, 2011, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalgebra.2010.11.004.
[12] P. Singh, Learn PySpark: Build Python-based machine learning and deep learning models. Apress, Berkeley, CA, pp. 1-210, 2019, https://books.google.co.id/books?id=3-GtDwAAQBAJ.
[13] R. S. Daulay, “Analisis Kritis dan Pengembangan Algoritma K-Nearest Neighbor (KNN): Sebuah Tinjauan Literatur,” J. Pendidik. Sains dan Komput., vol. 4, no. 02, pp. 131–141, 2024, https://doi.org/10.47709/jpsk.v4i02.5055.
[14] N. T. Ujianto, Gunawan, H. Fadillah, A. P. Fanti, A. D. Saputra, and I. G. Ramadhan, “Penerapan algoritma K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) untuk klasifikasi citra medis,” IT-Explore J. Penerapan Teknol. Inf. dan Komun., vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 33–43, 2025, https://doi.org/10.24246/itexplore.v4i1.2025.pp33-43.
[15] A. Upadhyay, S. Nadar, and R. Jadhav, “Comparative Study of SVM & KNN for Signature Verification,” J. Stat. Manag. Syst., vol. 23, no. 2, pp. 191–198, 2020, https://doi.org/10.1080/09720510.2020.1724619.
[16] V. S. Souza and D. A. Lima, “Cardiac Disease Diagnosis Using K-Nearest Neighbor Algorithm: A Study on Heart Failure Clinical Records Dataset,” Artif. Intell. Appl., vol. 3, no. 1, pp. 56–71, 2025, https://doi.org/10.47852/bonviewAIA42022045.
[17] K. L. Kohsasih, D. S. Sunario, A. Alvin and F. Laurendio, “Enhancing Early Heart Disease Detection Through Comparative Analysis of Random Forest , Decision Tree , and K-NN Models,” IT J. Res. Dev., vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 66–77, 2025. https://doi.org/10.25299/itjrd.2025.24703.
[18] T. A. Assegie, S. J. Sushma, B. G. Bhavya, and S. Padmashree, “Correlation Analysis for Determining Effective Data in Machine Learning: Detection of Heart Failure,” SN Comput. Sci., vol. 2, no. 3, pp. 1–5, 2021, https://doi.org/10.1007/s42979-021-00617-5.
[19] R. Yunus, U. Ulfa, and M. D. Safitri, “Application of the K-Nearest Neighbors (K-NN) Algorithm for Classification of Heart Failure,” J. Appl. Intell. Syst., vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 1–9, 2021, https://doi.org/10.33633/jais.v6i1.4513.
[20] A. D. Kumari, J. P. Kumar, V. S. Prakash, and K. S. Divya, “Supervised Learning Algorithms : A Comparison,” Kristu Jayanti J. of Comput. Sci., vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 1–12, 2020. https://doi.org/10.59176/kjcs.v1i1.1259.
[21] U. S. Reddy, A. V. Thota, and A. Dharun, “Machine Learning Techniques for Stress Prediction in Working Employees,” 2018 IEEE Int. Conf. Comput. Intell. Comput. Res. ICCIC 2018, 2018, https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCIC.2018.8782395.
[22] Z. Mushtaq, A. Yaqub, S. Sani, and A. Khalid, “Effective K-Nearest Neighbor Classifications for Wisconsin Breast Cancer Data Sets,” J. Chinese Inst. Eng., vol. 43, no. 1, pp. 80–92, 2020, https://doi.org/10.1080/02533839.2019.1676658.
[23] N. Hadianto, H. B. Novitasari, and A. Rahmawati, “Klasifikasi Peminjaman Nasabah Bank Menggunakan Metode Neural Network,” J. Pilar Nusa Mandiri, vol. 15, no. 2, pp. 163–170, 2019, https://doi.org/10.33480/pilar.v15i2.658.
[24] S. Ketu and P. K. Mishra, “Scalable kernel-based SVM classification algorithm on imbalance air quality data for proficient healthcare,” Complex Intell. Syst., vol. 7, no. 5, pp. 2597–2615, 2021, https://doi.org/10.1007/s40747-021-00435-5.